The World's Fusion Revolution Begins in Virginia
Virginia, a pioneer in nuclear energy since 1957, is once again making history. The Commonwealth will soon be home to the world's first commercial fusion power plant, marking a new era in clean energy production. This groundbreaking project-located in Chesterfield, VA and funded through the Virginia Clean Energy Innovation Bank (VCEIB) -cements our state's status as a global leader in energy innovation and technology.
Fusion energy, often called the "holy grail" of power generation, promises virtually limitless, clean, and safe energy. This development not only continues Virginia's legacy of nuclear innovation but also positions the Commonwealth at the forefront of solving global energy and environmental challenges. The project is expected to create numerous jobs, attract top talent, and solidify Virginia's role as a hub for cutting-edge energy and technological advancements.
America's Leader in Nuclear Energy
Nuclear isn't just the largest source of carbon-free electricity in the United States, it's also the most reliable source of energy we have. When the sun isn't shining and the wind isn't blowing, nuclear provides the affordable energy needed to keep the lights on.
America's journey with Nuclear began in Virginia in 1957, when the SM-1 Nuclear Reactor in Fort Belvoir became the first atomic power generator to produce electrical energy for the U.S. power grid. Sixty years later, Virginia remains a leader in nuclear technology and innovation. Over 95% of our carbon-free electricity comes from two nuclear power plants, and we are making investments in groundbreaking nuclear technologies to power our communities 24 hours a day, 365 days a year.
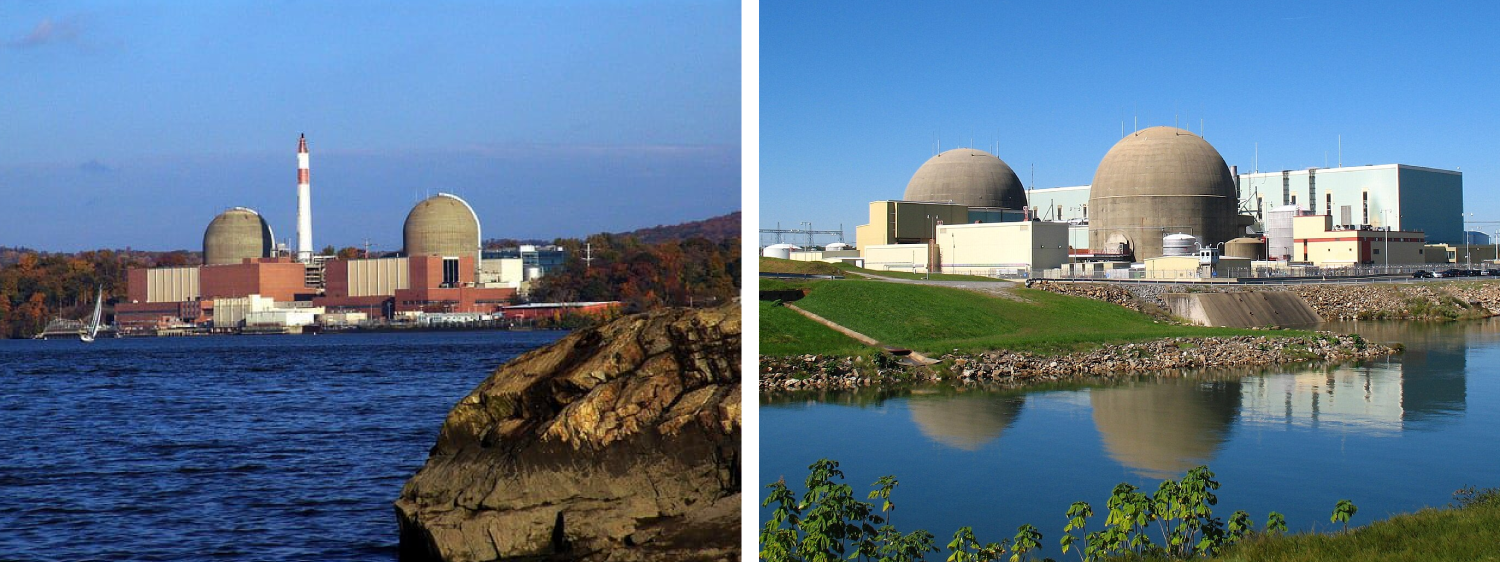

Virginia's Nuclear Future
In 2023, the Governor and the Virginia General Assembly created the Virginia Power Innovation fund and the Virginia Innovative Nuclear Hub to support the efforts to bring SMRs to the Commonwealth. This builds off existing initiatives like the Virginia Nuclear Energy Consortium Authority (VNECA) and the Virginia Nuclear Energy Consortium (VNEC), created in 2013 as part of the Commonwealth's long-term commitment to nuclear innovation.
Virginia Nuclear Energy Consortium Authority (VNECA)
VNECA's mission is to make the Commonwealth a national and global leader in nuclear energy and to serve as an interdisciplinary study, research and information resource for the Commonwealth on nuclear energy issues. Learn more about the authority.
The Virginia Nuclear Energy Consortium (VNEC)
VNEC is a public private group created alongside of the VNECA to represent stakeholders invested in the development of nuclear energy. These stakeholders include Virginia Department of Energy, colleges and universities, nuclear energy companies and suppliers and organizations that support the advancement of the nuclear industry. Learn more about the consortium.
Virginia Power Innovation Fund
The Virginia Energy Innovation Fund provides $4 million for research and development of innovative energy technologies, including nuclear, hydrogen, carbon capture and utilization and energy storage. Funds from this program support the Virginia Innovative Nuclear Hub (VIN Hub), which awards competitive grants to support workforce development, research, education, electrical generation, supply chain and advanced manufacturing.
Benefits:
Reliability:
Nuclear power plants generate energy around the clock, providing power when we need it the most.

Clean Energy:
Nuclear energy is as clean as it comes and is responsible for over half of the nation's carbon-free electricity.

Job Creation:
Nuclear energy supports about half a million jobs in the U.S. and adds roughly $60 billion to the national GDP annually.

Energy Efficiency:
Nuclear power plants generate huge amounts of energy using far less fuel than their fossil fuel.

Challenges:
While most Americans are in favor of nuclear energy and there is widespread bipartisan support for investments in Nuclear energy, nuclear isn't without its share of challenges. Thankfully, Virginia is uniquely positioned to face these challenges head on.
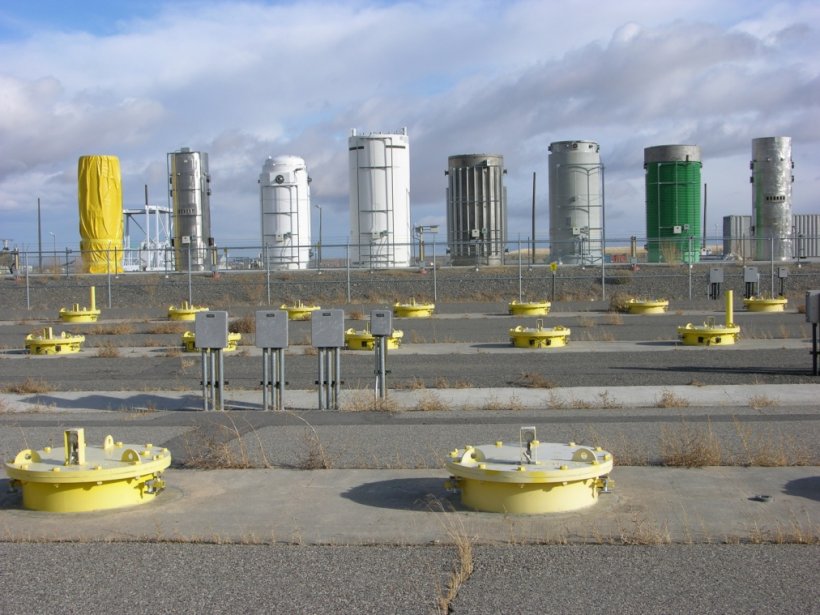
Spent Nuclear Fuel
Some people remain concerned about the transport, storage, and disposal of spent nuclear fuel. However, spent nuclear fuel is stored in some of the most technologically advanced facilities on earth with robust environmental safeguards, rigorous maintenance schedules, and extensive security operations.
Putting Communities First:
When planning for a new storage facility, the U.S. Department of Energy works closely with potential host communities to address any concerns they have and to determine whether hosting a storage facility aligns with the community's goals. This approach is known as "consent-based siting," and it is meant to keep communities engaged throughout the entire site selection process and to ensure any new facilities are in the best interest of all parties involved.
Learn more about Consent Based Siting.

Upfront Costs
Although Nuclear power plants produce far greater and more reliable energy than other renewable or traditional fuel sources, the initial startup costs for a nuclear power plant can be substantial.
Investing In Our Future:
Startup costs are a reality of any energy project. To mitigate these expenses, Virginia is exploring investments in next-generation technologies, such as small modular reactors (SMRs), which have the potential to drive down startup costs on nuclear projects. Public-private partnerships, federal incentives, and innovative financing models are a few of the other strategies that can be used to overcome financial hurdles.
Public Perceptions
Some people perceive commercial nuclear power as dangerous due to a lack of trustworthy information; an association of nuclear weapons with nuclear energy; negative or misinformed portrayals in popular media; and previous environmental disasters.
Your Partner in Virginia's Energy Future:
As Virginia continues to lead the nation in nuclear innovation, Virginia Energy is committed to dispelling common misconceptions and providing you with the unbiased facts you need to stay informed.
- Educational Resources: We're developing fact-based multimedia resources that address concerns, raise awareness, and correct common misconceptions.
- Program Updates:We're posting updates, timelines, presentations, and other resources to help communities stay on top of what is (and is not) happening with nuclear energy in Virginia.
- Community Meetings: We're on the ground with communities, providing a space for people to have their voices heard and their questions answered.
- Reliable, Affordable, & Clean: We've developed an energy plan for Virginia's future that ensures our lights stay on, our bills stay low, and our environment remains clean.
Nuclear Energy Safety
Safe Storage and Containment
Spent fuel storage in the United States employs the most sophisticated technologies and safety protocols available and is managed closely by the U.S. Department of Energy.
Robust containers built from materials that are impervious to corrosion and radiation serve as the first line of defense. These containers are then encased in thick barriers of concrete, forming an impenetrable shield against any potential escape of radioactive materials. These storage sites are heavily guarded and designed to withstand earthquakes, projectiles, tornadoes, floods, extreme temperatures, and more!
Looking forward, another promising technology for long-term spent fuel storage is geological repositories. These repositories use deep underground geological formations, such as stable rock formations or salt deposits, as natural barriers to contain radioactive waste. Countries like Finland and Sweden have made significant strides in establishing such repositories, with stringent safety protocols ensuring the integrity of these storage facilities for thousands of years.
Modern Reactors: Innovations in Safety
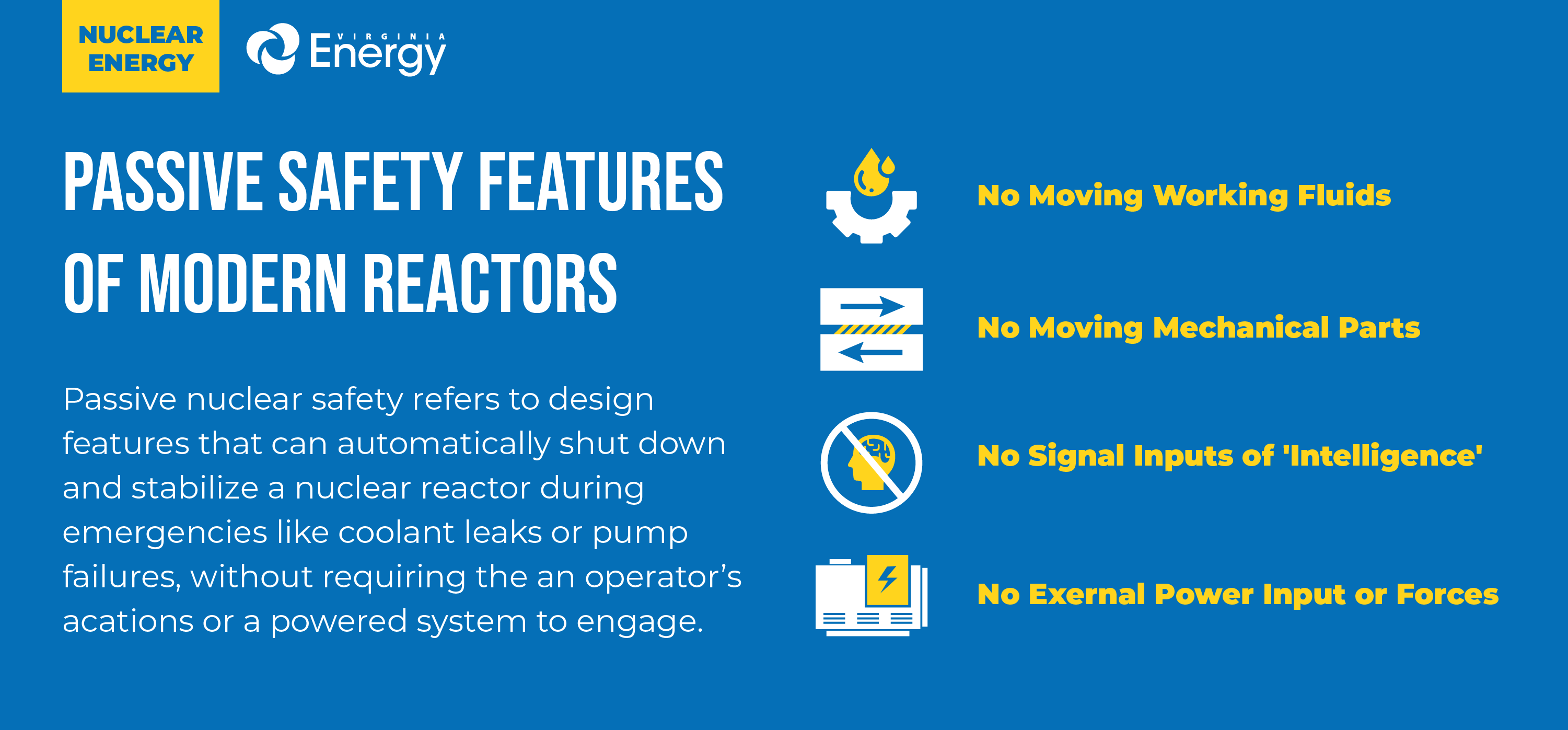
Modern nuclear reactors aren't like those built 50 years ago. Newly developed passive safety systems, redundant cooling mechanisms, and enhanced control systems are designed to prevent and mitigate accidents before they escalate.
Nuclear Fuel: Used, but Not Wasted
After nuclear fuel has been used, it still maintains over 90% of its energy potential, meaning that it can be recycled and used again. New reactors designs are being developed to maximize the use of recycled fuel which would yield even less waste than the highly efficient reactors in use today.
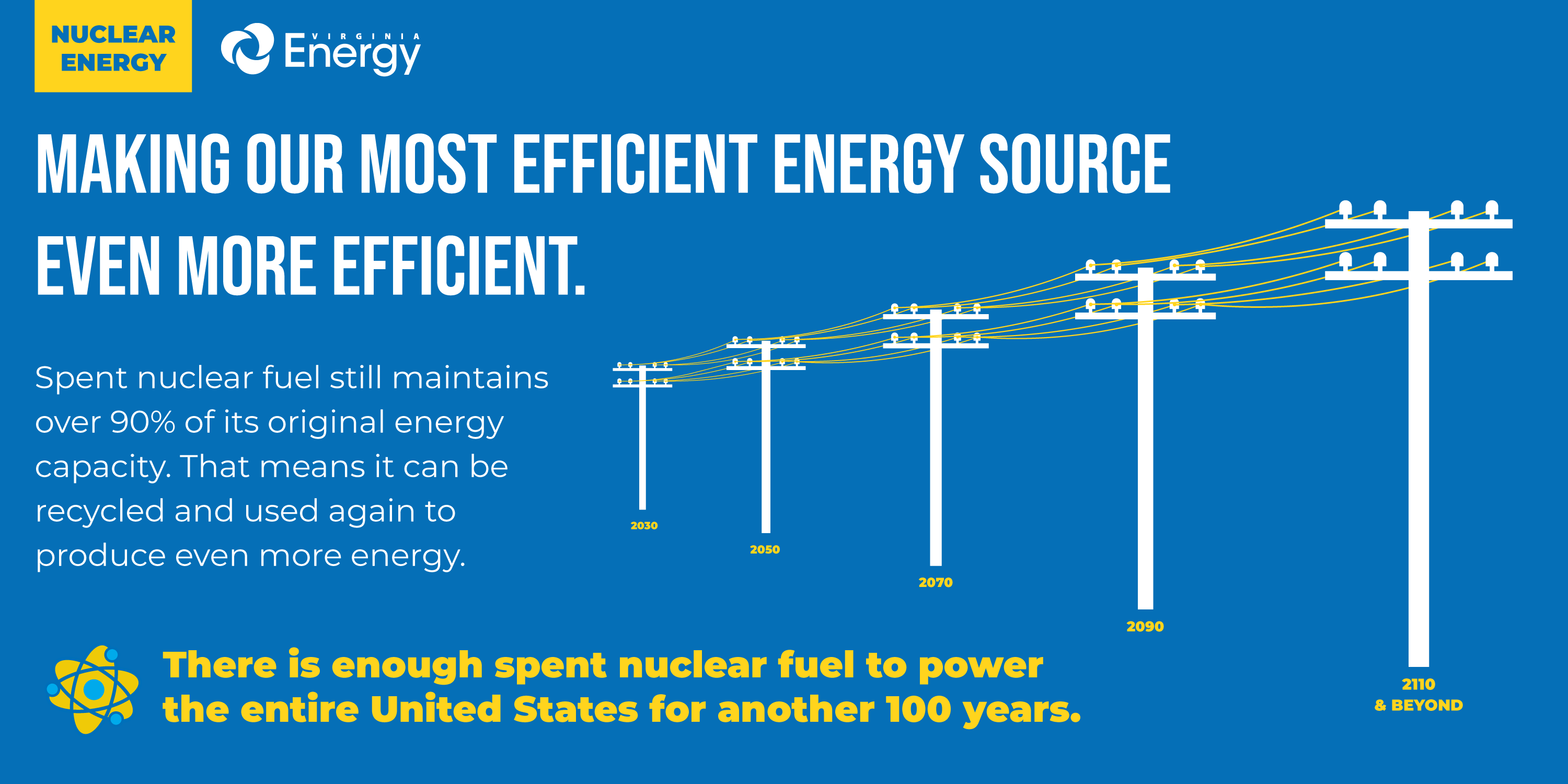
The US doesn't yet recycle its fuel, but other countries, such as France and Russia, do. As nuclear efforts take shape in the US, recycled fuel will be a critical component reducing the reliance on nuclear fuel sources, reducing costs, and increasing safety.
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)
In 2022, Governor Glenn Youngkin announced that Virginia would build a Small Modular Reactor (SMR) within the next 10 years, making the Commonwealth the first state to adopt this innovative technology to its grid.
Small modular reactors (SMRs) offer a transformative approach to nuclear energy, designed for factory assembly and easy transportation to site locations. Their compact size not only reduces initial startup costs and construction times, but also provides flexibility for deployment in regions with smaller electric grids or limited capacity for large-scale reactors.
This innovative approach promises to enhance energy accessibility while contributing to Virginia's affordable, reliable, and increasingly clean energy goals. More information on this exciting new technology is available from the U.S. Department of Energy.
Other Reactor Technologies
Light Water Reactor Technologies
The existing U.S. nuclear fleet of Light Water reactors has a remarkable safety and performance record. Extending the operating lifetimes of current plants beyond 60 years and, where possible, making further improvements in their productivity will generate early benefits from research, development, and demonstration investments in nuclear power. Learn more at the U.S. Department of Energy.
Advanced Reactor Technologies
As a result of Advanced Reactor Technologies (ARC) research, nuclear energy will continue to provide clean, affordable, and secure energy while supporting the administration's greenhouse gas reduction goals by introducing advanced designs into new energy and industrial markets. DOE will pursue RD&D on both advanced thermal and fast neutron spectrum systems. Learn more at the U.S. Department of Energy.
Versatile Test Reactor
In February 2019, the U.S. Department of Energy announced its plans to build a Versatile Test Reactor, or VTR. This new research reactor will be capable of performing irradiation testing at much higher neutron energy fluxes than what is currently available today. Learn more at the U.S. Department of Energy.
Educational Resources
Office of Nuclear Energy under the U.S. Department of Energy provides information on the latest research, news, and educational resources related to nuclear energy.
Nuclear Science Week presents a collection of resources and activities centered on nuclear science for educators and students.
Navigating Nuclear by the American Nuclear Society provides a dynamic program with digital lesson plans, career profiles, and virtual field trips to explore nuclear science's impact on various fields.
The Ultimate Fast Facts Guide to Nuclear Energy offers key information about nuclear power's role in America's clean energy production and its reliability as an energy source.
Nuclear & Uranium Data by the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) features plant-specific data and statistics on nuclear electricity generation and capacity.
Understanding the Societal Challenges Facing Nuclear Power by the National Academies Press includes educational materials to communicate the findings of their report to stakeholders and non-specialist audiences.
U.S. Nuclear Plants by the Nuclear Energy Institute provides national and state statistics for nuclear energy and details on local plants.
Map of U.S. Nuclear Plants shows the location and electricity output of nuclear plants across the country.
World Nuclear Association offers detailed reports and information on the status and development of nuclear power worldwide.


